Blow molding vs. injection molding—what’s the difference? Both are common methods used to create plastic parts. And while some parts require both blow-molded and injection-molded components—for example, a medical device with a blow-molded container attached to an injection molded apparatus, or a military application with a blow-molded “payload” packet fabricated inside an injection molded projectile—the two methods primarily serve different markets.
The main similarity between them is that, before the molding process can begin, you must have a mold with the shape of the part you want inside it. The mold is most typically made of steel (though some parts may require another material) and is created with tight part tolerances (+/- .0005 of an inch). This keeps the plastic in an injection mold or a blow mold from flashing (seeping into crevices) and creates a quality part.
Below are the basic steps manufacturers take for blow molding vs. injection molding.
Blow Molding
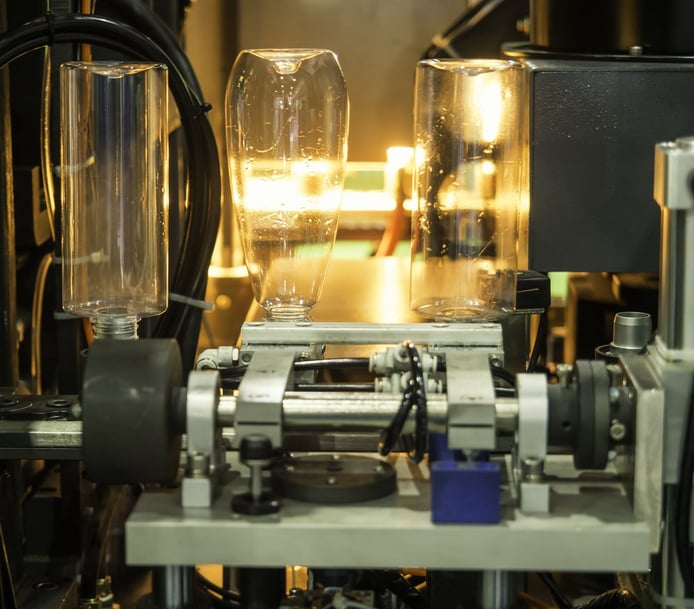
Blow molding is a specialized type of plastic processing used to create hollow plastic parts. The most common type of blow molding is called extrusion blow molding, which is used to create plastic bottles or other hollow containers.
To create a blow-molded product, manufacturers perform the following steps:
- The completed mold is placed in the blow molding machine.
- A parison (also known as a preform), which is a tube of plastic with one hole that allows air to funnel through, is heated until it becomes soft.
- The molten parison is placed into a blow mold that is cooler in temperature.
- An air tube is inserted into the hole in the parison.
- The mold is closed, and the air inside the parison blows the molten plastic (similar to blowing up a balloon) until the plastic forms to the shape of the mold.
- Once the part has cooled, the mold opens and the completed part is ejected from the mold.
The most notable drawback of blow molding is that it’s very difficult to create a precise, uniform part, because it’s essentially impossible to get the plastic to thin out evenly as air blows through it. Consider a milk jug; the handle is often the thickest part, but the walls of the jug vary in thickness from top to bottom. That said, uniformity isn’t typically an issue for plastic bottles, as they are produced in mass quantities and are primarily used as containers.
Injection Molding
Unlike blow molding, which can only create a hollow part, injection molding can be used to create a solid plastic part or a hollow part (through gas-assisted injection molding, for example).
To create an injection-molded product, manufacturers perform the following steps:
- The completed mold is placed in the injection molding machine.
- The plastic pellets are heated until they are liquid.
- The liquid plastic goes through a dryer, if necessary (as moisture in the plastic might cause splay or hydrolysis in the finished product).
- The liquid plastic is conveyed into the injection molding machine through a vacuum.
- The liquid plastic goes through a heated injection barrel, which is attached to a feed throat.
- The liquid plastic is injected under pressure through the feed throat into a mold.
- The mold—which is cooler than the liquid plastic—causes the plastic material to cool to a solid state, which forms the plastic part.
- The mold opens and the cooled plastic part is ejected from the mold either by hand (in a vertical injection molding machine) or by force of gravity (in a horizontal injection molding machine).
Take the first step toward creating your injection-molded part.
Fill out the form below and we’ll get a conversation started about how Micron can help you take your concept or prototype to production. We are committed to providing an excellent experience for our customers, including shorter lead times, improved part quality, and exceeding your expectations. Fill out the short form below or contact us and we’ll be in touch.



